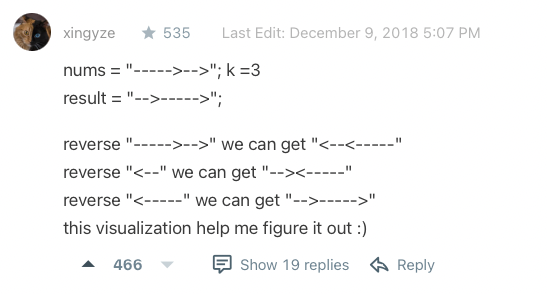
Medium 189. Rotate Array link
Solution#1: using extra space to store some elements which will be covered when rotating. 𝒪(n ) Space and time complexity.
Solution #2: reverse three times on original array and only cost 𝒪(1) space.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public :void rev (int l,int r,vector<int > &n) while (l < r) {swap (n[l],n[r]);void rotate (vector<int >& nums, int k) size ();rev (0 ,nums.size ()-1 ,nums);rev (0 ,k-1 ,nums);rev (k,nums.size ()-1 ,nums);
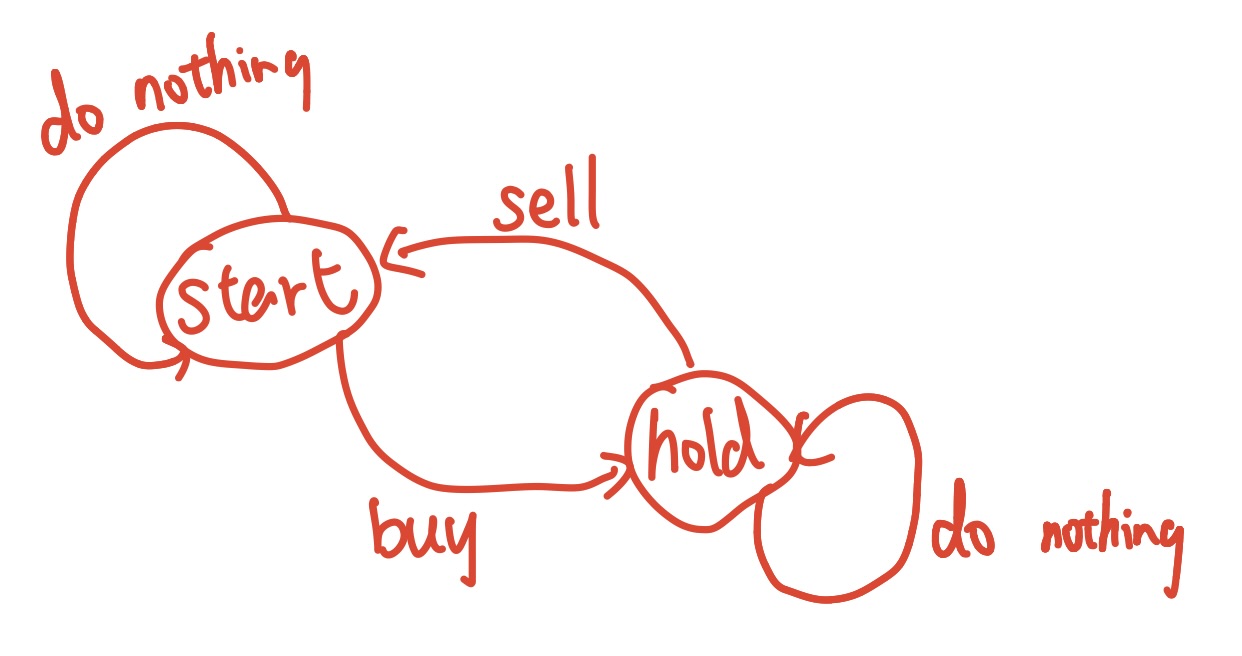
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II (no limit on how many times you can buy&sell)
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with transaction fee
122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
309. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Cooldown class Solution {public :int maxProfit (vector<int >& prices) int >> pf (2 ,vector<int >(3 ,0 ));0 ][1 ] = 0 -prices[0 ];for (int i=1 ;i< prices.size ();i++) {1 ][0 ] = max (pf[0 ][0 ],pf[0 ][2 ]);1 ][1 ] = max (pf[0 ][1 ],pf[0 ][0 ] - prices[i]);1 ][2 ] = pf[0 ][1 ] + prices[i];0 ] = pf[1 ];return max (max (pf[0 ][0 ],pf[0 ][1 ]),pf[0 ][2 ]);
Jump Game II DP solution 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public :int jump (vector<int >& nums) vector<int > dp (nums.size(),INT32_MAX) ;0 ] = 0 ;int farthest = 0 ;for (int i=0 ;i<nums.size ();i++) {if (i+nums[i] <= farthest) continue ;for (int j=i+1 ;j<=i+nums[i];j++) {if (j >= nums.size ()) break ;min (dp[j],dp[i]+1 );return dp[nums.size ()-1 ];
Greedy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public :int jump (vector<int >& nums) int steps = 0 ;int farthest = 0 ,thres=0 ;for (int i=0 ;i<nums.size ()-1 ;i++) {max (farthest,i+nums[i]);if (i == thres) {if (farthest >= nums.size ()-1 ) break ;return steps;
Group Anagrams using hashmap with several optimizations main idea: hashmap which maps the sorted string to grouped anagrams.
Line 5: using unordered_map because the sequence doesn’t matters.
Line 11: reserve() to avoid reallocate
Line 13: using std::move to avoid copy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public :groupAnagrams (vector<string>& strs) {for (string &s:strs) {sort (s.begin (), s.end ());push_back (cpy);reserve (m.size ());for (pair<const string,vector<string>> &p:m) {push_back (std::move (p.second));return ans;
tricks since the string only includes lower-case alphabets, using this sort function is faster.
string strSort (string s) {int counter[26 ] = {0 };for (char c : s) {'a' ]++;for (int c = 0 ; c < 26 ; c++) {string (counter[c], c + 'a' );return t;
intuition 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 class Solution {public :inline bool cmp (map<char ,int > &l,map<char ,int > &r) for (pair<const char ,int >& pr:l) {if (r.find (pr.first) == r.end () || pr.second != r[pr.first]) return false ;return true ;groupAnagrams (vector<string>& strs) {int > idx;if (strs.size () == 0 ) return ans;sort (strs.begin (), strs.end (),[](string &l,string &r) {return l.length () < r.length ();char ,int >> v;for (string & str : strs) {char ,int > m;for (char &ch:str) {push_back (m);push_back ({strs[0 ]});push_back (0 );bool flag;for (int i=1 ;i<strs.size ();++i) {false ;for (int j=ans.size ()-1 ;j>=0 ;j--) {if (ans[j][0 ].length () == strs[i].length ()) {if (cmp (v[idx[j]], v[i])) {push_back (strs[i]);true ;break ;if (!flag) {push_back ({strs[i]});push_back (i);return ans;
424. Longest Repeating Character Replacement Sliding window
In line 10, using if is enough because the sliding window only violates the restriction by one character.
Ans 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public :int characterReplacement (string s, int k) vector<int > v (26 ,0 ) ;int l=0 ,r=0 ;int maxl=0 ;int maxc = 0 ;for (;r<s.length ();r++) {max (maxc, ++v[s[r]-'A' ]);if (r-l+1 - maxc > k) {'A' ];max (maxl,r-l+1 );return maxl;
435. Non-overlapping Intervals https://leetcode.com/problems/non-overlapping-intervals/discuss/91713/Java:-Least-is-Most/730443
105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal //TBD
300. Longest Increasing Subsequence DP solution class Solution {public :int lengthOfLIS (vector<int >& nums) vector<int > dp (nums.size(),1 ) ;for (int i=0 ;i<nums.size ();i++) {for (int j=0 ;j<i;j++) {if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {max (dp[i],dp[j] + 1 );return *max_element (dp.begin (),dp.end ());
Greedy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public :int lengthOfLIS (vector<int >& nums) int > ans;int n=nums.size ();int >::iterator it;for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++) {lower_bound (begin (ans),end (ans),nums[i]);if (it == end (ans)) {push_back (nums[i]);else {return ans.size ();
REF:
[C++/Python] DP, Binary Search, BIT Solutions - Picture explain - O(NlogN) - LeetCode Discuss
LongestIncreasingSubsequence.pdf
209. Minimum Size Subarray Sum Solution 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public :int minSubArrayLen (int target, vector<int >& nums) int n = nums.size ();int ans = INT_MAX;vector<int > sum (n+1 ,0 ) ;for (int i=1 ;i<=n;++i) {-1 ] + sum[i-1 ];for (int i=n;i>0 && sum[i] >= target; i--) {int j = upper_bound (begin (sum),end (sum), sum[i] - target) - begin (sum);min (ans, i-j+1 );return ans == INT_MAX ? 0 : ans;
Solution 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 impl Solution {pub fn min_sub_array_len i32 , nums: Vec <i32 >) -> i32 {let mut ans = 200000 ;for lb in 0 ..nums.len() {let mut sum = 0 ;for rb in lb..nums.len() {if sum >= target {1 );break ;if ans == 200000 {0 else {as i32
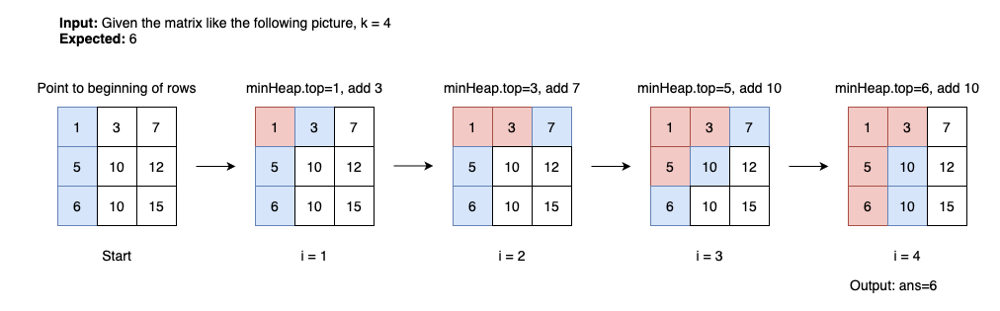
378. Kth Smallest Element in a Sorted Matrix Solution #1: min heap [C++/Java/Python] MaxHeap, MinHeap, Binary Search - Picture Explain - Clean & Concise - LeetCode Discuss
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 typedef pair<int ,pair<int ,int >> pr;class Solution {public :int n;int kthSmallest (vector<vector<int >>& matrix, int k) size ();auto cmp = [](pr &l, pr &r){return l.first > r.first; decltype (cmp)> pq (cmp);for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++) {push ({ matrix[i][0 ], { i,0 } });for (int i=0 ;i<k-1 ;i++) {int ,int > ax = pq.top ().second;pop ();if (ax.second + 1 < n) pq.push ( {matrix[ax.first][ax.second+1 ], {ax.first,ax.second+1 }} return pq.top ().first;
Solution #2 Binary Search 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 typedef pair<int ,pair<int ,int >> pr;class Solution {public :int n;int ans=0 ;int kthSmallest (vector<vector<int >>& matrix, int k) size ();int l = matrix[0 ][0 ];int r = matrix[n-1 ][n-1 ];int mid;int tmp;while (l <= r) {2 ;num (mid,matrix);if (tmp >= k) {-1 ; else {1 ;return ans;int num (int thres,vector<vector<int >>& m) int count = 0 ;int col = n-1 ;for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++) {while (col >= 0 && m[i][col] > thres) col--;1 );return count;
Subset 力扣
DFS 每一位数字可以选或者不选。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public :int >> ans;int len;void dfs (int pos, vector<int >& path, vector<int >& nums) if (pos == len) {push_back (path);return ;dfs (pos+1 ,path,nums);push_back (nums[pos]);dfs (pos+1 ,path,nums);pop_back ();int >> subsets (vector<int >& nums) {sort (begin (nums),end (nums));size ();vector<int > path (0 ) ;dfs (0 ,path,nums);return ans;
状压 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public :int >> ans;int len;int >> subsets (vector<int >& nums) {size ();int lim = (1 <<len);int > v;reserve (20 );for (int i=0 ;i<lim;i++) {for (int j=0 ;j<len;j++) {if ( (i & (1 << j) )) v.push_back (nums[j]);push_back (v);clear ();return ans;
525. Contiguous Array find the maximum length of contiguous subarray with an equal number of 0 and 1.
Prefix Sum + HashMap 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public :int findMaxLength (vector<int >& nums) int len = nums.size ();vector<int > prefix (len+1 ,0 ) ;int ,int > um={{0 ,0 }};int ans = 0 ;for (int i=1 ;i<=len;i++) {if (nums[i-1 ]) prefix[i] = prefix[i-1 ] + 1 ;else prefix[i] = prefix[i-1 ] - 1 ;if (um.find (prefix[i]) != um.end ()) {max (ans,i-um[prefix[i]]);else {return ans;
560. Subarray Sum Equals K find the number of subarrays whose sum equals to k
Prefix Sum 加到目前的前缀和是pre。
用hashmap寻找前缀和是pre-k的数目,两个前缀之间的subarray就是和为k的subarray
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public :int subarraySum (vector<int >& nums, int k) int len = nums.size ();int pre = 0 ;int ,int > um={{0 ,1 }};int ans = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i<len ; i++) {if (um.find (pre-k) != um.end ()) {return ans;
148. 排序链表 D&C + Merge Sort 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 class Solution {public :ListNode* mergeSort (ListNode* head,ListNode* tail=nullptr ) {if (head->next == tail) return head;while (fast != tail && fast->next != tail) {mergeSort (head,slow);mergeSort (slow,tail);nullptr ;while (l1 != slow && l2 != tail) {if (l1->val < l2->val) {if (head == nullptr ) {else {else {if (head == nullptr ) {else {while (l1 != slow) {while (l2 != tail) {return head;ListNode* sortList (ListNode* head) {if (head == nullptr ) return nullptr ;return mergeSort (head);
Faster Version: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 class Solution {public :ListNode* mergeSort (ListNode* head,ListNode* tail=nullptr ) {if (head->next == tail) return head;while (fast != tail && fast->next != tail) {mergeSort (head,slow);mergeSort (slow,tail);nullptr ;if (l1->val < l2->val) {else {while (l1 != slow && l2 != tail) {if (l1->val < l2->val) {else {if (l1 != slow) {while (cursor->next != slow) cursor=cursor->next;else if (l2 != tail){while (cursor->next != tail) cursor=cursor->next;return head;ListNode* sortList (ListNode* head) {if (head == nullptr ) return nullptr ;return mergeSort (head);
1868. Product of Two Run-Length Encoded Arrays
坑点:
如果当前两个数的乘积和之前一样的话,直接把 frequency 累加到前面而不是 push_back 一个新的 element
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {public :int >> findRLEArray (vector<vector<int >>& encoded1, vector<vector<int >>& encoded2) {int p1 = 0 ;int s1 = encoded1.size ();int p2 = 0 ;int s2 = encoded2.size ();int prod,freq;int >> ans;while (p1 < s1 && p2 < s2) {0 ] * encoded2[p2][0 ];min (encoded1[p1][1 ],encoded2[p2][1 ]);if (!ans.empty () && prod == ans.back ()[0 ]) {back ()[1 ] += freq;else {push_back ({prod,freq});if (encoded1[p1][1 ] == freq) {else {1 ] -= freq;if (encoded2[p2][1 ] == freq) {else {1 ] -= freq;return ans;
146. LRU Cache Implement the LRUCache
LRUCache(int capacity) initialize the Cache with positive size.int get(int key) return the value of key. void put(int key,int value) update the value at key. If the number of keys exceeds the capacity, evict the least recently used key.
get and put should run in O(1) time complexity.
How to?
When an item is accessed, it should be “marked” as most recent used item. Doubly linked list can remove and insert in constant time. Each time the item is accessed, it is moved to the front of the linked list.
Query? We use a hashmap to store <key, pointer> pair. The pointer points to the node of linked list.
Note that:
When a node is removed, its key in the hashtable should also be removed.
Dummy nodes can be used to reduce the complexity of insert and remove operation.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 class LRUCache {public :class Node {public :int ,int > kv;Node (Node* p1= nullptr ,Node* p2= nullptr ):prev (p1),next (p2){}Node (int k,int v,Node* p1= nullptr ,Node* p2= nullptr ):kv ({k,v}),prev (p1),next (p2){}int capacity;int count;int ,Node*> um;int remove_head () int key = node_delete->kv.first;delete node_delete;return key;Node* insert (int key,int val) {new Node (key,val,prev,dummy_tail);return new_node;void move_to_front (Node* node) LRUCache (int capacity) {this ->capacity = capacity;this ->count = 0 ;new Node (nullptr ,new Node ());int get (int key) if (um.find (key) == um.end ()) return -1 ;move_to_front (um[key]);return um[key]->kv.second;void put (int key, int value) if (um.find (key) != um.end ()) {move_to_front (um[key]);else { if (count == capacity) {int removed_key = remove_head ();erase (removed_key);insert (key,value);